Understanding Endothelial Function and Its Importance
Before diving into how Telmisartan improves endothelial function, it's essential to understand what endothelial function is and why it's crucial for our health. The endothelium is a thin layer of cells lining the inside of our blood vessels. It plays a vital role in maintaining vascular health by regulating blood pressure, blood clotting, and the formation of new blood vessels. When the endothelium becomes dysfunctional, it can lead to various cardiovascular diseases, such as hypertension, atherosclerosis, and heart attacks.
In this article, we will explore the different ways Telmisartan, a popular medication for hypertension, helps improve endothelial function and, in turn, promotes overall cardiovascular health. Read on to learn about the science behind this powerful drug.
Telmisartan: A Potent Angiotensin Receptor Blocker
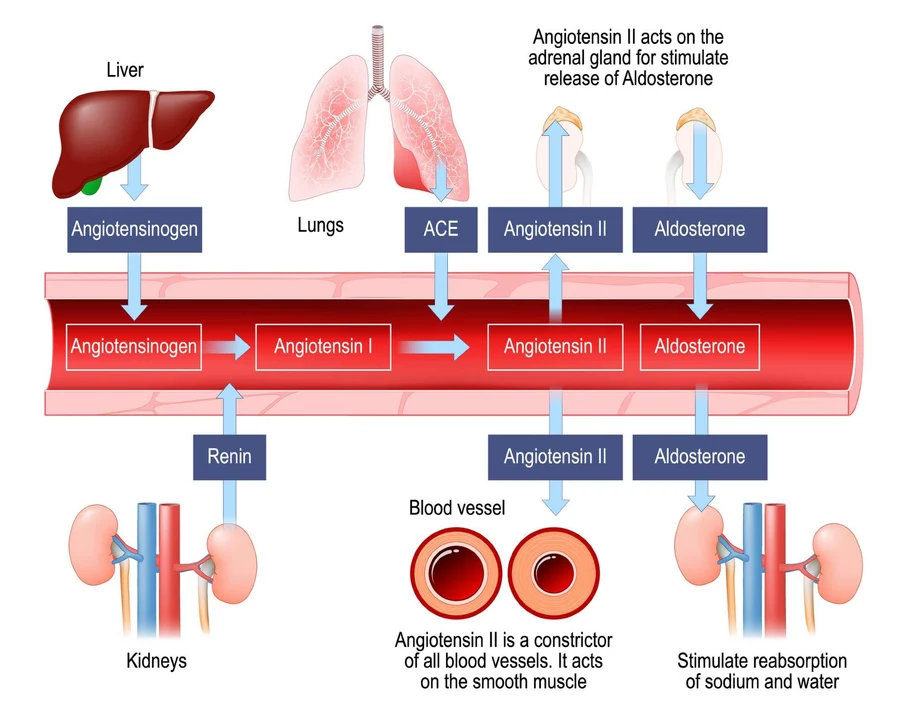
Telmisartan belongs to a class of medications called angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs). These drugs work by blocking the action of a hormone called angiotensin II, which is responsible for constricting blood vessels and raising blood pressure. By inhibiting the effects of angiotensin II, Telmisartan helps relax blood vessels, lower blood pressure, and ultimately improve endothelial function.
But what sets Telmisartan apart from other ARBs? The answer lies in its unique chemical structure and additional pharmacological properties that contribute to its ability to enhance endothelial function beyond just lowering blood pressure.
Reducing Oxidative Stress and Inflammation
Oxidative stress and inflammation are two significant factors that contribute to endothelial dysfunction. Telmisartan has been shown to possess antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties that help mitigate these harmful effects. By reducing the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and inflammatory cytokines, Telmisartan helps preserve the function and integrity of endothelial cells, thereby improving overall endothelial function.
Furthermore, Telmisartan has been found to stimulate the production of nitric oxide (NO), a molecule that plays a critical role in maintaining blood vessel health. NO helps relax blood vessels, prevents blood clot formation, and inhibits the growth of smooth muscle cells that contribute to atherosclerosis. By promoting NO production, Telmisartan further enhances endothelial function and cardiovascular health.
Improving Insulin Sensitivity and Glucose Metabolism
Impaired insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism are known to contribute to endothelial dysfunction. Interestingly, Telmisartan has been shown to improve insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism in various studies, potentially through its ability to activate peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPAR-γ), a protein involved in regulating glucose and lipid metabolism.
By enhancing insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism, Telmisartan can indirectly improve endothelial function and reduce the risk of developing diabetes-related vascular complications.
Preventing Atherosclerosis and Reducing Plaque Formation
Atherosclerosis, the buildup of fatty deposits and plaques in the arteries, can lead to reduced blood flow and ultimately cause heart attacks and strokes. Telmisartan has been shown to help prevent atherosclerosis and reduce plaque formation by inhibiting the proliferation of smooth muscle cells and the expression of adhesion molecules on endothelial cells. These actions help maintain the elasticity and integrity of blood vessels, thereby promoting proper endothelial function.
Moreover, Telmisartan's ability to lower blood pressure also plays a role in preventing atherosclerosis, as high blood pressure can damage blood vessel walls and contribute to plaque buildup.
Enhancing Endothelial Progenitor Cell Function
Endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) are responsible for repairing and regenerating damaged endothelial cells. Telmisartan has been found to enhance the function of EPCs by increasing their survival, proliferation, and ability to form new blood vessels. This effect is crucial in maintaining a healthy endothelium and preventing the progression of endothelial dysfunction.
Furthermore, Telmisartan's impact on EPC function may also contribute to its ability to improve endothelial function in patients with cardiovascular risk factors, such as hypertension, diabetes, and obesity.
Conclusion: Telmisartan as a Comprehensive Treatment for Endothelial Dysfunction
In summary, Telmisartan's multifaceted approach to improving endothelial function makes it an excellent choice for managing hypertension and reducing the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Its ability to lower blood pressure, reduce oxidative stress and inflammation, improve insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism, prevent atherosclerosis, and enhance endothelial progenitor cell function all contribute to its effectiveness in promoting overall vascular health.
If you or a loved one are experiencing hypertension or other cardiovascular risk factors, it's essential to speak with your healthcare provider about the best treatment options, which may include Telmisartan. Remember that maintaining a healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and managing stress are also vital components of good cardiovascular health.

12 Comments
Michael J Ryan
April 29, 2023 AT 08:08Great rundown! Telmisartan seems to wear many hats, from lowering pressure to giving our EPCs a boost. It's awesome when a drug can multitask like this. Keep the science coming!
Khalil BB
May 2, 2023 AT 19:28Telmisartan's hype is overblown; it's just another ARB masquerading as a miracle.
Keri Shrable
May 6, 2023 AT 06:48Wow, this drug sounds like a superhero cape for our blood vessels! 🌟 It swoops in, cuts down the oxidative villains and lifts the NO‑levels sky‑high! The way it nudges insulin sensitivity is like giving your metabolism a friendly pep‑talk! Plus, the EPC boost? That’s like hiring extra repair crews on a highway! Thanks for the clear breakdown!
Destiny Hixon
May 9, 2023 AT 18:08Our own meds should do the job, not some foreign pharma hype. Telmisartan does the trick, just trust the science we got here. No need to chase pricey imported drugs.
mike brown
May 13, 2023 AT 05:28Sounds like marketing fluff to me.
shawn micheal
May 16, 2023 AT 16:48I totally get that any extra tool against hypertension feels like a win. The anti‑inflammatory angle of Telmisartan is especially promising for folks battling both high blood pressure and chronic inflammation. It’s also reassuring to see the drug positively affect glucose metabolism-dual benefits are always a bonus. If you’re on it, sharing your experience can help others decide whether it’s right for them.
Stephen Jahl
May 20, 2023 AT 04:08Telmisartan, as an angiotensin II type 1 receptor antagonist, exerts primary antihypertensive effects through vascular smooth muscle relaxation.
Beyond hemodynamic modulation, it interacts with intracellular signaling cascades that influence oxidative stress pathways.
Empirical evidence indicates a downregulation of NADPH oxidase activity, thereby diminishing reactive oxygen species generation.
Concomitantly, the upregulation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase augments nitric oxide bioavailability, fostering vasodilation.
The anti‑inflammatory milieu is further reinforced by attenuation of nuclear factor‑κB transcriptional activity.
Such molecular interferences translate clinically into improved flow‑mediated dilation metrics in endothelial function assessments.
Moreover, telmisartan’s partial agonism of peroxisome proliferator‑activated receptor‑γ orchestrates favorable alterations in lipid and glucose homeostasis.
This pleiotropic profile contributes to insulin sensitization, a factor of paramount relevance in patients with metabolic syndrome.
The drug’s influence on endothelial progenitor cell viability is mediated through Akt phosphorylation, promoting cellular proliferation.
Enhanced EPC mobilization underpins reparative angiogenesis, a process that mitigates atherogenic progression.
Clinical trials have demonstrated a statistically significant reduction in carotid intima‑media thickness among telmisartan‑treated cohorts.
Nevertheless, the heterogeneity of study designs necessitates cautious extrapolation to broader populations.
Adverse event profiles remain comparable to other ARBs, with hyperkalemia and renal function perturbations being the most notable.
Therapeutic adherence is often bolstered by the drug’s once‑daily dosing convenience.
In summation, telmisartan embodies a multifaceted pharmacologic entity that transcends mere blood pressure control.
Future investigations should elucidate the long‑term cardiovascular outcomes associated with its endothelial protective actions.
gershwin mkhatshwa
May 23, 2023 AT 15:28Seeing all these mechanisms laid out makes it clear why telmisartan is a go‑to for many clinicians. It’s not just blood pressure; it’s about protecting the whole vascular ecosystem. If you’re curious about side effects, most people tolerate it well, but always check with your doc.
Louis Robert
May 27, 2023 AT 02:48Telmisartan offers a multi‑pronged approach to endothelial health.
tim jeurissen
May 30, 2023 AT 14:08While the article is comprehensive, it conflates correlation with causation in a few instances, notably when attributing plaque reduction solely to ARB activity without accounting for confounding lifestyle variables.
lorna Rickwood
June 3, 2023 AT 01:28Maybe but the data does suggest an effect though the exact mechanism could be more complex
Nick Ham
June 6, 2023 AT 12:48The mechanistic overview is dense yet lacks critical appraisal of clinical trial heterogeneity.