Telmisartan: Uses, Doses, Side Effects, and Practical Tips
Want clear, practical facts about telmisartan? This short guide covers what telmisartan does, common doses, side effects to watch for, key interactions, and safe buying tips. No fluff—just the points that matter when you're taking or considering this blood pressure medicine.
How telmisartan works and who takes it
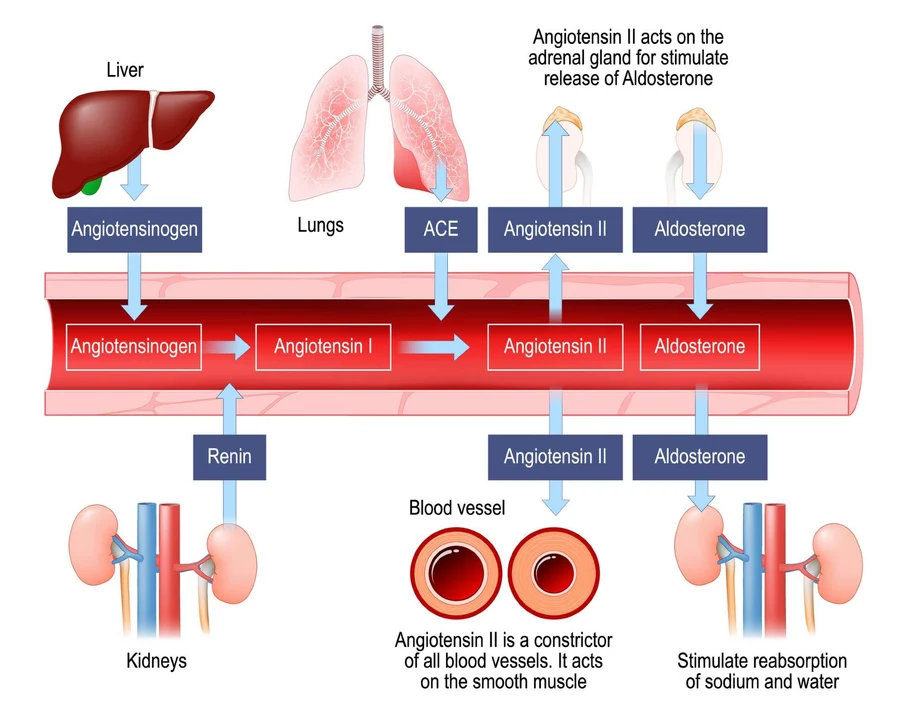
Telmisartan is an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB). It relaxes blood vessels so blood flows easier, which lowers blood pressure. Doctors commonly prescribe it for hypertension and to reduce cardiovascular risk in some patients. It’s often chosen when people can’t tolerate ACE inhibitors since it rarely causes the dry cough that ACE inhibitors can cause. Telmisartan has a long action, so it’s normally taken once a day.
Common tablet strengths are 20 mg, 40 mg, and 80 mg. Typical starting doses are 20–40 mg once daily; many patients reach 40–80 mg depending on response. It can be combined safely with a diuretic or a calcium channel blocker when a single drug doesn’t control blood pressure.
Practical tips: dosing, monitoring, interactions
Take telmisartan at the same time every day, with or without food. If you miss a dose, take it as soon as you remember unless it’s almost time for the next dose—don’t double up. Expect possible lightheadedness in the first days; sit or lie down if you feel dizzy. Check your blood pressure at home and tell your doctor about big drops or fainting.
Your doctor will usually check kidney function and potassium within 1–2 weeks after starting or changing the dose, then periodically after that. Telmisartan can raise potassium (hyperkalemia) and rarely affect kidney function, so lab checks matter. Older adults may be more sensitive to low blood pressure, so clinicians often start at a lower dose.
Watch drug interactions: avoid combining telmisartan with potassium supplements or potassium-sparing diuretics unless closely monitored. Regular NSAID use (ibuprofen, naproxen) can reduce telmisartan’s effect and increase kidney risk. Combining ARBs with ACE inhibitors or with direct renin inhibitors raises the chance of low blood pressure, kidney problems, and high potassium—do not combine these without specialist guidance. Tell your provider about all prescription drugs, over-the-counter meds, and supplements.
Important safety notes: do not take telmisartan if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant—ARBs can harm the fetus. If you breastfeed, ask your doctor whether to stop the drug or switch to another treatment. If you have severe liver disease or certain kidney artery problems, telmisartan may not be suitable.
Thinking of buying telmisartan online? Use only licensed pharmacies that require a prescription, show clear contact details, and offer pharmacist access. Avoid sites that sell without a prescription or offer unusually low prices. If in doubt, ask your clinic for a recommended pharmacy or use a verified national service.
Simple questions to ask your prescriber: What starting dose is right for me? When will you check my blood tests? What side effects should make me stop the drug? Getting answers to these keeps treatment safe and effective.
How Telmisartan Improves Endothelial Function
In my latest blog post, I discussed the impressive benefits of Telmisartan in improving endothelial function. Telmisartan, an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB), has been shown to significantly enhance blood flow and circulation by reducing inflammation and oxidative stress. This, in turn, leads to better vascular health and overall cardiovascular function. Additionally, Telmisartan has the potential to lower blood pressure and prevent heart-related complications. It's crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any treatment, but it's exciting to see the promising effects of Telmisartan on our body's vascular system.
© 2026. All rights reserved.