Diabetes: Practical Tips for Managing Blood Sugar and Medication
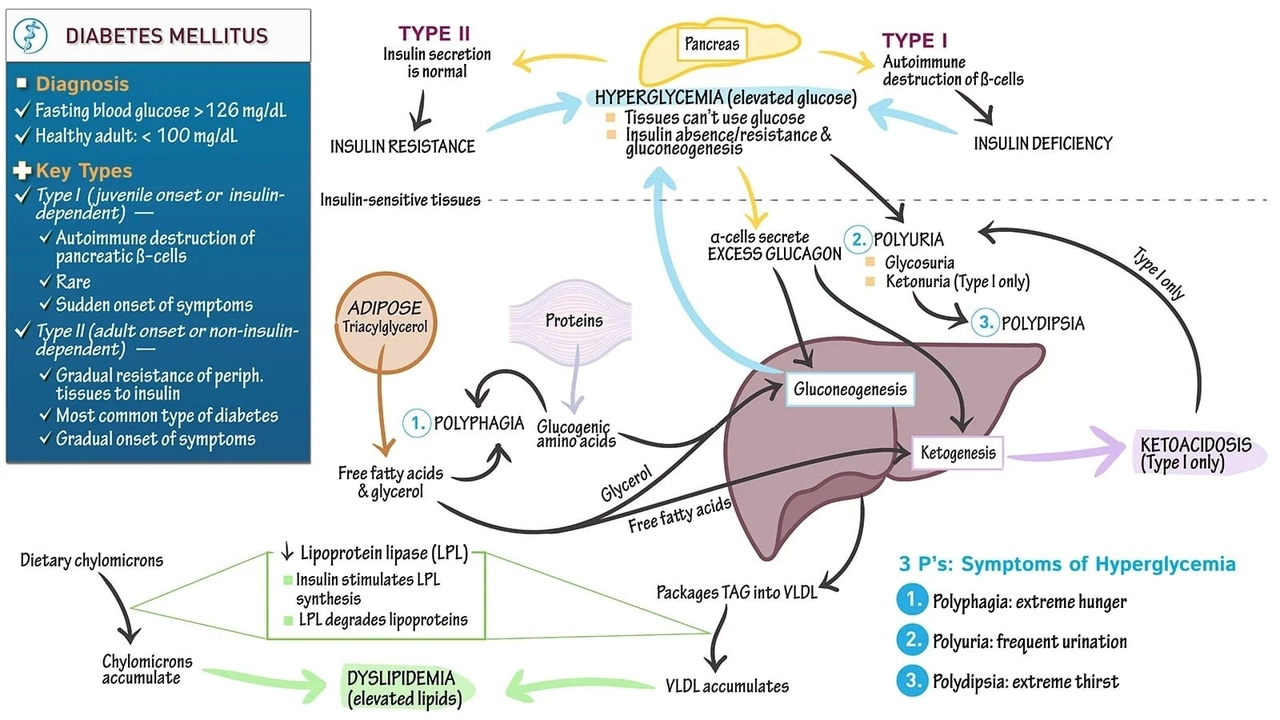
Diabetes affects millions and managing it well makes daily life easier. You don’t need perfect numbers every day, but steady control prevents worries and complications. Here I give clear, practical steps you can use now: testing, meds, food, and simple habits that matter.
Start with monitoring. Check your blood sugar when your doctor suggests and learn what your numbers mean. For many people continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) helps spot trends you miss with finger checks. CGM can show how meals, exercise, or delayed stomach emptying from diabetic gastroparesis change your sugar. If your readings swing without clear reason, talk to your care team about testing for gastroparesis and adjusting meds or meal timing.
Medication matters. Metformin is a common first choice for type 2 diabetes, while insulin or other injectables may be needed for type 1 or advanced type 2. Take meds exactly as prescribed and never skip doses because you feel better. If side effects bother you, discuss alternatives, doctors can switch doses or try other drug classes that fit your life better.
Food and routines help more than you might think. Aim for regular meal times, balanced portions, and protein with carbs to slow glucose spikes. Small changes like swapping white bread for whole grain, adding a cup of vegetables, or moving after meals can lower spikes without big sacrifices. Carb counting matters if you take insulin; simple apps can make this straightforward.
Move a little every day. Exercise improves insulin sensitivity and can be a short walk, cycling, or even household tasks. Start with 10 to 20 minutes and build up. If you have neuropathy, choose low-impact options like swimming or stationary bike.
Read labels and stay safe online. If you order medications or supplies online, use verified pharmacies and keep prescriptions. Cheap sites may sell fake insulin or wrong doses. Look for clear contact details, pharmacist access, and secure checkout. When in doubt, ask your local pharmacy to verify the product.
Watch for warning signs. High blood sugar can cause thirst, fatigue, blurred vision, or frequent urination. Low sugar brings sweating, shaking, confusion, or irritability. Keep fast carbs for lows and wear medical ID if you use insulin or have severe lows.
Plan for travel and life changes. Carry extra supplies, keep insulin cool in hot weather, and store prescriptions in your carry-on. Tell coworkers or family how to help during a low blood sugar event.
Work with your team. Regular checkups, A1C tests, foot exams, and eye screening catch problems early. Bring a list of questions to appointments and track readings between visits.
If you want more focused guides, like CGM use in gastroparesis, buying supplies online safely, or choosing the right medication, explore our diabetes articles below. Clear, practical advice is here to help you manage diabetes with less stress and more confidence.
Subscribe for updates, or use our search to find latest medication guides, CGM tips, and verified online pharmacy reviews for diabetes supplies right now. Learn more.
Edema and Diabetes: Causes, Complications, and Management
Edema and diabetes are closely related, as high blood sugar levels can cause fluid retention, leading to swelling in various body parts. This condition can be quite uncomfortable, and if left untreated, can lead to serious complications such as cellulitis and impaired blood flow. To manage edema in diabetic patients, it's essential to maintain proper blood sugar levels, reduce salt intake, and engage in regular physical activity. Compression stockings and elevation of swollen limbs may also provide relief. Remember, always consult your healthcare provider for personalized medical advice and treatment.
© 2026. All rights reserved.